Key Concepts
Essential terminology and ideas from The Selfish Gene, explained clearly with visual examples.
Gene-Centered View of Evolution
Gene
The fundamental unit of heredity and natural selection. In "The Selfish Gene," Dawkins argues that genes, not individuals or species, are the primary units of natural selection. Genes that enhance their own survival chances will be selected for, even if they do not benefit the organism as a whole.
Replicator
An entity capable of making copies of itself. Dawkins introduces this concept to explain how life began with simple molecules that could replicate themselves. Genes are the most significant replicators in biological evolution.
Vehicle
The organism that carries and protects the genes. According to Dawkins, organisms are merely "survival machines" or vehicles built by genes to ensure their continued replication and spread.
Altruism and Selfishness
Altruism
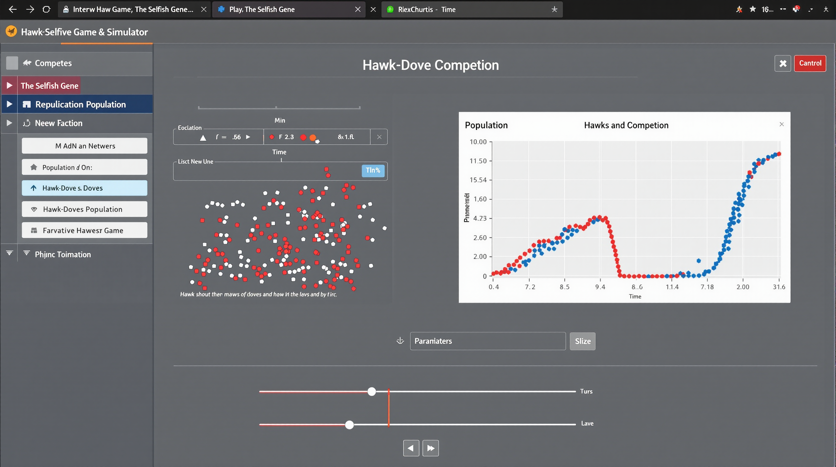
Behavior that benefits others at a cost to oneself. In evolutionary biology, this refers to an organism reducing its own fitness to increase the fitness of another organism. Dawkins explains that altruistic behavior can evolve if it helps copies of an individual's genes in other organisms (usually relatives).
Reciprocal Altruism
A form of altruism where organisms help others with the expectation of receiving help in return. This explains how cooperation can evolve between unrelated individuals. The concept was further developed by Robert Trivers but is discussed by Dawkins as a mechanism for cooperation.
Kinship and Inclusive Fitness
Inclusive Fitness
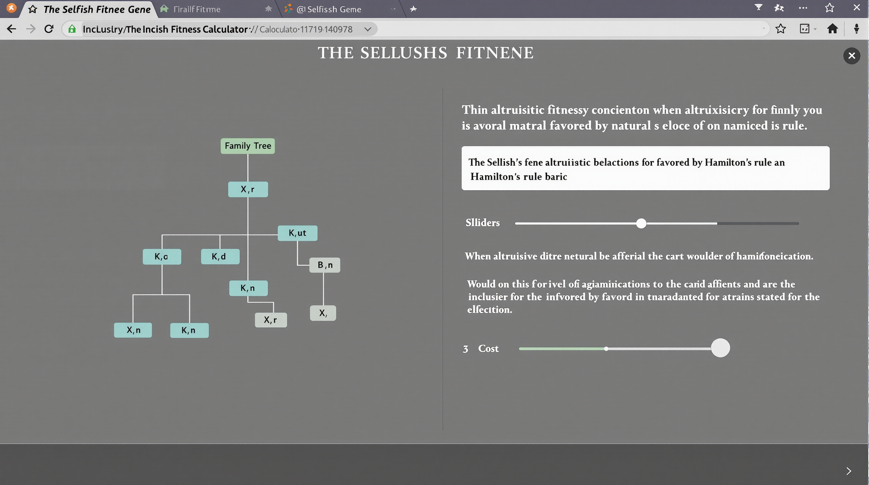
An extension of the fitness concept that includes an organism's ability to promote the reproduction of related individuals who share their genes. This explains why animals might sacrifice themselves for close relatives — they are helping copies of their own genes to survive in those relatives.
Hamilton's Rule
A mathematical rule formulated by W.D. Hamilton stating that altruistic behavior will be favored by natural selection when rB > C, where r is the genetic relatedness of the recipient to the actor, B is the reproductive benefit gained by the recipient, and C is the reproductive cost to the actor.